How to set up an aquarium sump is a question many fish enthusiasts ask, especially those looking to enhance their aquarium’s filtration and overall health. Sumps, essentially external filter systems, offer a powerful way to manage water quality, promote beneficial bacteria growth, and even house additional filtration components like refugiums or bio-pellet reactors.
This guide will walk you through the process of setting up your own aquarium sump, from choosing the right components to understanding the plumbing and filtration methods.
Setting up a sump is a rewarding experience that can greatly improve your aquarium’s health and aesthetics. It’s an investment in the well-being of your aquatic pets, allowing you to create a more stable and vibrant environment for them to thrive in.
This guide will equip you with the knowledge and steps needed to successfully set up your own sump system, whether you’re a seasoned aquarist or just starting out.
Setting Up the Sump: How To Set Up An Aquarium Sump
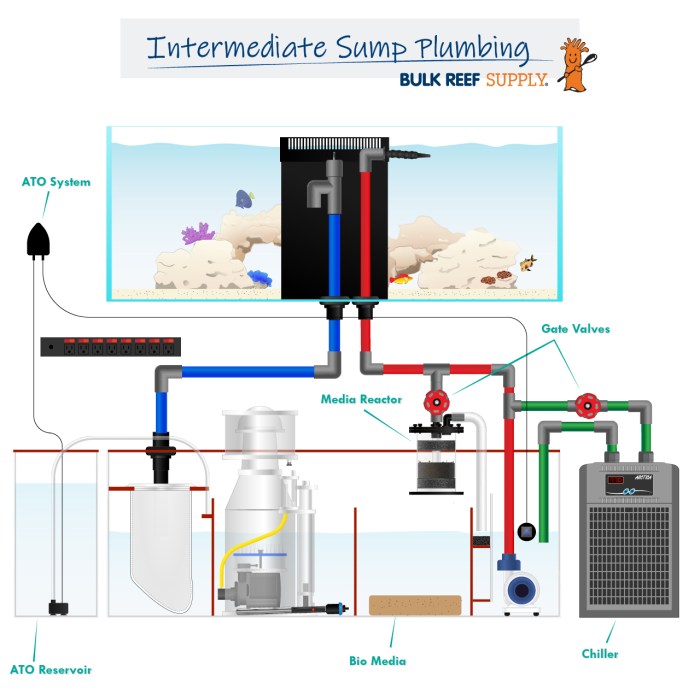
Setting up a sump is a crucial step in establishing a healthy and efficient aquarium environment. A sump acts as a filtration system, housing essential components that remove waste, enhance water clarity, and create a stable ecosystem for your aquatic inhabitants.
Sump Components
A sump typically comprises several essential components that work in unison to achieve optimal water quality. These components are:
- Pump:The pump is the heart of the sump system. It draws water from the main tank through an overflow box and pushes it into the sump. The pump’s flow rate should be sufficient to handle the volume of water in your aquarium.
- Overflow Box:The overflow box is a crucial component that safely directs excess water from the main tank into the sump. It prevents the aquarium from overflowing and ensures a constant water level. Overflow boxes come in various designs, including traditional, external, and internal types.
- Return Line:The return line is the conduit that carries filtered water from the sump back to the main tank. It is typically equipped with a spray bar or other devices to distribute the water evenly and create gentle currents.
- Filter Media:The sump houses various filter media that remove waste and impurities from the water. Common filter media include mechanical, chemical, and biological media. Mechanical media, such as filter floss, traps large debris, while chemical media, such as activated carbon, removes dissolved pollutants.
Biological media, such as bio-balls or ceramic rings, provide a surface area for beneficial bacteria to colonize, breaking down harmful ammonia and nitrite into less toxic nitrates.
- Skimmer:A protein skimmer is a valuable addition to a sump system, especially for saltwater aquariums. It removes dissolved organic waste and proteins, enhancing water clarity and reducing nutrient levels. Protein skimmers use a venturi system to create tiny bubbles that attract and remove these impurities.
- Refugium:A refugium is a section of the sump dedicated to growing macroalgae. These algae consume excess nutrients in the water, contributing to a healthier ecosystem and reducing the need for frequent water changes.
Sump Construction Materials
Sumps are commonly constructed using two primary materials:
- Acrylic:Acrylic is a popular choice for sump construction due to its lightweight, transparent, and durable nature. It is relatively easy to work with, making it suitable for custom-built sumps. However, acrylic can scratch easily, requiring careful handling.
- Glass:Glass is another common material used for sump construction. It offers excellent clarity and durability, making it a reliable choice for long-term use. However, glass is heavier than acrylic and can be more challenging to work with, making custom-built glass sumps more expensive.
Sump Plumbing and Filtration
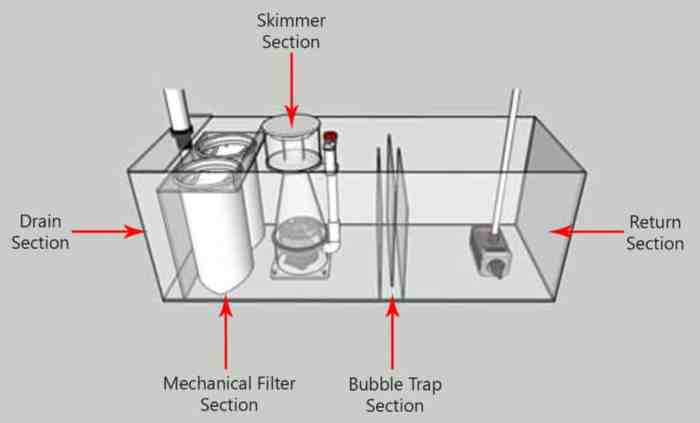
The plumbing and filtration systems in your sump are essential for maintaining a healthy aquarium environment. A well-designed sump system effectively removes waste, provides mechanical and chemical filtration, and promotes beneficial bacteria growth for biological filtration.
Sump Plumbing Design
A typical sump plumbing system involves several components, including the return pump, overflow box, drain pipes, and various plumbing fittings. Here is a diagram of a typical sump system:[Diagram of a sump plumbing system]The diagram shows the flow of water from the aquarium to the sump and back.
The overflow box siphons water from the aquarium into the sump. The return pump pushes the filtered water back to the aquarium. The drain pipes allow for water to flow from the sump to the drain or to the various filtration stages.
Sump Plumbing Fittings
Various plumbing fittings are used in sump setups to connect different components and create a secure and efficient system. Here are some common types of fittings:
- Bulkheads:These are threaded fittings that are installed in the aquarium or sump wall to allow for pipes to be connected. They provide a watertight seal and are essential for connecting drain pipes, return lines, and other components.
- Elbows:These fittings allow for changes in the direction of the plumbing lines. They come in various angles, such as 90 degrees, 45 degrees, and 180 degrees, to accommodate different plumbing configurations.
- T-fittings:These fittings allow for the splitting of a plumbing line into two separate branches. They are commonly used to create multiple filtration stages or to connect drain lines to the sump.
- Union fittings:These fittings allow for the easy disconnection of plumbing lines without the need for cutting or dismantling the entire system. They are useful for maintenance or repairs.
- Valves:Valves are used to control the flow of water through the plumbing system. They allow for adjustments in water flow rates, shut-off, and isolation of specific sections of the plumbing.
Filtration Methods in Sumps
Sump filtration systems often incorporate various methods to remove different types of waste and pollutants from the aquarium water. These methods work in conjunction to provide a comprehensive and efficient filtration system.
- Mechanical Filtration:This method involves physically removing solid waste particles from the water. Mechanical filters are typically placed in the first stage of the sump and consist of materials like filter floss, sponges, and filter pads. These materials trap debris, reducing the workload on the biological and chemical filters.
- Chemical Filtration:This method removes dissolved pollutants and impurities from the water. Chemical filters often contain activated carbon, which absorbs dissolved organic compounds, toxins, and medications. Chemical filtration helps improve water clarity and reduces the buildup of harmful substances.
- Biological Filtration:This method relies on beneficial bacteria to break down ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate, the primary waste products produced by fish and other aquatic life. Biological filters are typically housed in the last stage of the sump and contain a large surface area for bacteria to colonize.
This can be achieved using bio-media, such as ceramic rings, lava rock, or filter balls.
The order of filtration stages in a sump is important. Mechanical filtration should be the first stage to remove large particles, followed by chemical filtration to remove dissolved impurities, and finally, biological filtration to break down toxic waste products.
Setting up an aquarium sump involves creating a separate chamber for mechanical, biological, and chemical filtration. While you’re ensuring your fish have a healthy environment, consider their diet too. Did you know that goldfish can enjoy a healthy snack of carrots?
Can Goldfish Eat Carrots: A Guide to Safe Veggie Treats provides helpful information on feeding your goldfish vegetables. Once your sump is in place, you’ll have a thriving ecosystem, complete with a well-nourished and happy goldfish population.
Sump Maintenance and Troubleshooting
A well-maintained sump is crucial for a healthy aquarium ecosystem. Regular cleaning and troubleshooting ensure optimal water quality and prevent potential problems. This section covers essential maintenance tasks and provides guidance on addressing common sump issues.
Sump Maintenance Checklist
Regular sump maintenance is essential to keep your aquarium healthy. This checklist Artikels key tasks to perform on a routine basis:
- Weekly:Inspect the sump for any debris or algae buildup. Remove any visible debris with a siphon or net. Check the water level and top off as needed.
- Monthly:Clean the mechanical filtration media (e.g., filter floss, sponges) using a gentle water stream. Remove any accumulated debris. Rinse the biological filtration media (e.g., ceramic rings, bio-balls) with aquarium water to avoid disrupting beneficial bacteria.
- Quarterly:Thoroughly clean the sump, including all components and plumbing. This involves removing and cleaning the mechanical and biological filtration media, as well as scrubbing the sump chamber and any attached equipment. Inspect the sump plumbing for leaks or blockages.
- Annually:Replace worn-out or damaged sump components, such as filter floss, sponges, and mechanical filtration media. Inspect and clean the protein skimmer, and replace the impeller if necessary.
Troubleshooting Common Sump Problems, How to set up an aquarium sump
Sump problems can indicate underlying issues in your aquarium ecosystem. This section provides tips for diagnosing and addressing common sump issues:
- Low Water Level:Check for leaks in the sump or plumbing. Ensure the return pump is functioning correctly and not drawing too much water. Top off the sump with freshwater as needed.
- Cloudy Water:This usually indicates an overgrowth of bacteria or algae. Increase water changes, clean the mechanical filtration media, and ensure proper aeration.
- High Nitrate Levels:Overfeeding, excessive waste, or insufficient biological filtration can contribute to high nitrate levels. Reduce feeding, increase water changes, and ensure the biological filtration media is functioning correctly.
- Smell:A foul odor often indicates a buildup of waste or rotting organic matter. Clean the sump thoroughly, check for any dead fish or invertebrates, and ensure proper aeration.
- Noise:A noisy sump may indicate a malfunctioning pump, clogged filter media, or air trapped in the plumbing. Check the pump for debris, clean the filter media, and inspect the plumbing for air leaks.
Cleaning and Replacing Sump Components
Properly cleaning and replacing sump components is essential for maintaining water quality and ensuring the longevity of your aquarium. This section Artikels the steps for cleaning and replacing common sump components:
Cleaning Mechanical Filtration Media
Mechanical filtration media, such as filter floss and sponges, trap debris and particulate matter. Cleaning these media is essential to prevent clogging and maintain water clarity.
- Remove the filter floss or sponge from the sump.
- Rinse the media under a gentle stream of aquarium water.Avoid using tap water, as it can introduce harmful chemicals into your aquarium.
- Squeeze out excess water from the media.
- Replace the cleaned media back into the sump.
Cleaning Biological Filtration Media
Biological filtration media, such as ceramic rings and bio-balls, house beneficial bacteria that break down waste products. Cleaning these media should be done carefully to avoid disrupting the beneficial bacteria.
- Remove the biological filtration media from the sump.
- Rinse the media with aquarium water.Avoid using tap water, as it can kill the beneficial bacteria.
- Do not squeeze or scrub the media vigorously.
- Replace the cleaned media back into the sump.
Replacing Filter Floss and Sponges
Filter floss and sponges should be replaced regularly, as they can become clogged with debris and lose their effectiveness.
- Remove the old filter floss or sponge from the sump.
- Replace with new filter floss or sponge of the appropriate size.
Cleaning and Replacing Protein Skimmers
Protein skimmers remove organic waste from the water. Cleaning and replacing components of the protein skimmer is essential for its optimal performance.
- Remove the skimmer cup and clean it thoroughly.
- Rinse the skimmer body and impeller with freshwater.
- Inspect the skimmer impeller for wear and tear.Replace the impeller if necessary.
- Reassemble the protein skimmer and adjust the water level.
Choosing the Right Sump for Your Aquarium
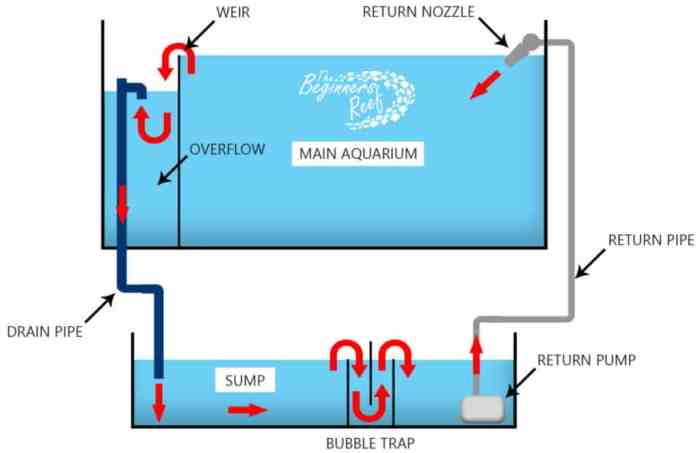
A sump is a crucial component of a well-functioning aquarium, providing ample space for filtration, water management, and equipment. Choosing the right sump for your aquarium is essential for ensuring its optimal performance and maintaining a healthy environment for your aquatic life.
Sump Size and Aquarium Size
The size of the sump should be appropriately scaled to the size of your aquarium. A general rule of thumb is to choose a sump that is approximately 20% to 30% of the volume of your aquarium. This allows for sufficient space for filtration media, water volume, and equipment.
| Aquarium Size (Gallons) | Recommended Sump Size (Gallons) |
|---|---|
| 10-20 | 2-4 |
| 20-40 | 4-8 |
| 40-60 | 8-12 |
| 60-80 | 12-16 |
| 80-100 | 16-20 |
| 100+ | 20+ |
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Sump
Several factors should be considered when selecting a sump for your aquarium, including:
- Tank Size:The size of your aquarium is the primary determinant of the appropriate sump size. A larger tank will require a larger sump to accommodate the filtration needs and water volume.
- Fish Load:The number and type of fish you keep will impact the filtration demands of your aquarium. A higher fish load will require a larger sump to handle the increased waste production.
- Filtration Needs:Different types of aquariums have different filtration needs. For example, saltwater aquariums require more robust filtration than freshwater aquariums.
- Space Availability:The available space beneath your aquarium will determine the size and shape of the sump you can accommodate.
- Budget:Sumps come in a wide range of prices, so it’s essential to consider your budget when making a decision.
Examples of Sump Setups for Various Aquarium Types
The design and setup of your sump will vary depending on the type of aquarium you have. Here are some examples of sump setups for different aquarium types:
- Freshwater Aquarium:A basic freshwater sump setup may include a mechanical filtration stage (e.g., filter floss), a biological filtration stage (e.g., bio-media), and a refugium (e.g., live rock or plants) for additional nutrient export.
- Saltwater Aquarium:Saltwater aquariums often require more robust filtration. A typical sump setup for a saltwater aquarium may include multiple stages of mechanical filtration, biological filtration, a refugium, and a protein skimmer.
- Planted Aquarium:Planted aquariums typically benefit from a sump with a large refugium to promote plant growth and reduce nutrient levels in the water.
Final Thoughts
Setting up an aquarium sump can seem daunting at first, but with careful planning and the right equipment, it’s a manageable process that can significantly improve your aquarium’s performance. By understanding the purpose of each component, the filtration methods, and the essential maintenance steps, you can create a healthy and thriving environment for your aquatic companions.
So, dive into the world of aquarium sumps and discover the benefits they offer, from improved water quality to enhanced aesthetics, all while ensuring a happier and healthier habitat for your fish.